RAPID PROTOTYPING
RAPID PROTOTYPING
SERVICE
SERVICE
manufacturing sample parts of your product to test for component fit, function, manufacturability, appearance, and strength

What are the Different Types of Rapid Prototyping?
Following are the types of rapid prototyping technology available for engineering product designers:
Stereolithography (SLA) or Vat Photopolymerization
This fast and affordable technique was the first successful method of commercial 3D printing. It uses a bath of photosensitive liquid which is solidified layer-by-layer using a computer-controlled ultra violet (UV) light.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Used for both metal and plastic prototyping, SLS uses a powder bed to build a prototype one layer at a time using a laser to heat and sinter the powdered material. However, the strength of the parts is not as good as with SLA, while the surface of the finished product is usually rough and may require secondary work to finish it.
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) or Material Jetting
This inexpensive, easy-to-use process can be found in most non-industrial desktop 3D printers. It uses a spool of thermoplastic filament which is melted inside a printing nozzle barrel before the resulting liquid plastic is laid down layer-by-layer according to a computer deposition program. While the early results generally had poor resolution and were weak, this process is improving rapidly and is fast and cheap, making it ideal for product development.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) or Powder Bed Fusion
Often known as powder bed fusion, this process is favoured for making high-strength, complex parts. Selective Laser Melting is frequently used by the aerospace, automotive, defence and medical industries. This powder bed based fusion process uses a fine metal powder which is melted in a layer by layer manner to build either prototype or production parts using a high-powered laser or electron beam. Common SLM materials used in RP include titanium, aluminium, stainless steel and cobalt chrome alloys.
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) or Sheet Lamination
This inexpensive process is less sophisticated than SLM or SLS, but it does not require specially controlled conditions. LOM builds up a series of thin laminates that have been accurately cut with laser beams or another cutting device to create the CAD pattern design. Each layer is delivered and bonded on top of the previous one until the part is complete.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Similar to SLA, this technique also uses the polymerisation of resins which are cured using a more conventional light source than with SLA. While faster and cheaper than SLA, DLP often requires the use of support structures and post-build curing.
Binder Jetting
This technique allows for one or many parts to be printed at one time, although the parts produced are not as strong as those created using SLS. Binder Jetting uses a powder bed onto which nozzles spray micro-fine droplets of a liquid to bond the powder particles together to form a layer of the part.
Each layer may then compacted by a roller before the next layer of powder is laid down and the process begins again. When complete the part may be cured in an oven to burn off the binding agent and fuse the powder into a coherent part.
What is Rapid Prototyping ?
Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer aided design (CAD) data.Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or "additive layer manufacturing" technology.
Rapid prototyping technology integrates mechanical engineering, CAD, reverse engineering technology, layered manufacturing technology, numerical control technology, material science, laser technology, which can automatically, directly, quickly and accurately transform the design idea into a functional prototype or direct manufacturing parts, so as to provide a high efficiency and low cost implementation means for parts prototyping, new design idea verification and other aspects.
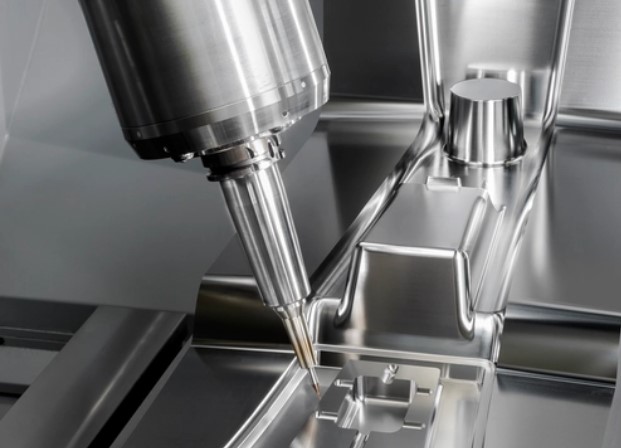

Which method is most commonly used for rapid prototyping?
3D Printing
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process ㅡ which means it involves adding portions of materials in layers to form the desired prototype. It is the most common method for rapid prototyping because of its high accuracy, material compatibility, and low cost (especially for a low volume of parts).
However, 3D printing technologies come in several types, each having its capability and suitability for different prototyping needs.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing method that involves using molds to create prototypes. To create prototypes using an injection molding machine, your manufacturer will first create a mold in the shape of your desired product. Next, the manufacturer heats up a thermoplastic polymer, changing it to molten fluid. This fluid is then injected into the mold cavity through a runner system to form the desired shape.
Injection molding is compatible with many materials (thermoplastics, metals, and liquid silicone rubber) and can create complex product designs. However, it is usually ideal for producing several replicas of a prototype, especially when you need to perform a series of tests on these prototypes.
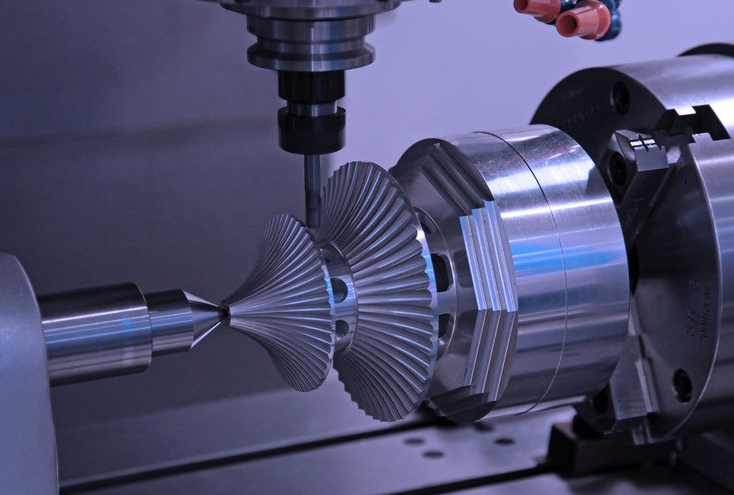
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing method ㅡ which means it creates the desired prototype by removing portions of material from a workpiece using cutting tools. Computer numerical control (CNC) technology automates the cutting tool’s and workpiece’s sequence of movement to create your prototypesCNC machining is generally the best rapid prototyping method for metal parts, especially when you need to create highly accurate functional prototype products

Which method is most commonly used for rapid prototyping?
3D Printing
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process ㅡ which means it involves adding portions of materials in layers to form the desired prototype. It is the most common method for rapid prototyping because of its high accuracy, material compatibility, and low cost (especially for a low volume of parts).
However, 3D printing technologies come in several types, each having its capability and suitability for different prototyping needs.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing method that involves using molds to create prototypes. To create prototypes using an injection molding machine, your manufacturer will first create a mold in the shape of your desired product. Next, the manufacturer heats up a thermoplastic polymer, changing it to molten fluid. This fluid is then injected into the mold cavity through a runner system to form the desired shape.
Injection molding is compatible with many materials (thermoplastics, metals, and liquid silicone rubber) and can create complex product designs. However, it is usually ideal for producing several replicas of a prototype, especially when you need to perform a series of tests on these prototypes.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing method ㅡ which means it creates the desired prototype by removing portions of material from a workpiece using cutting tools. Computer numerical control (CNC) technology automates the cutting tool’s and workpiece’s sequence of movement to create your prototypesCNC machining is generally the best rapid prototyping method for metal parts, especially when you need to create highly accurate functional prototype products
Advantage &Disadvantage of Rapid Prototyping
Saving Product Development Costs| Rapid prototyping lets you turn your concept into a test subject quickly and efficiently.Shorten new product development cycle, to ensure that new product time-to-market .it saves model or mold manufacturing time of the several times or even dozens of times.
Improve the ability of manufacturing of complex parts| made it possible for direct manufacturing of complex model ;
Eliminating the Risk of Product Failure| If your product designers discover major issues during the testing phase, these critical design flaws can be remedied before your product hits the market.
Significantly improve the success rate of new product launch| find the mistakes of product design in time and make early changes to avoid the large amount of losses caused by the changes of subsequent processes
Support the implementation of the synchronous (parallel) project | Make design, communication and evaluation more visualized, new product design, sample manufacturing, market ordering, production preparation, and other work can be carried out in parallel.
Support technological innovation, improve product appearance design| it is conducive to optimize the product design, industrial design is especially important for that.
Reduce the costly design flaws|Prototyping allows product designers to identify potential product safety and/or compliance issues. From form to function, this stage is where you can get to the root of any risk factors involved in your design. Multiplied to reduce the cost of new product development .
Improve the ability of manufacturing of complex parts| made it possible for direct manufacturing of complex model ;
Eliminating the Risk of Product Failure| If your product designers discover major issues during the testing phase, these critical design flaws can be remedied before your product hits the market.
Significantly improve the success rate of new product launch| find the mistakes of product design in time and make early changes to avoid the large amount of losses caused by the changes of subsequent processes
Support the implementation of the synchronous (parallel) project | Make design, communication and evaluation more visualized, new product design, sample manufacturing, market ordering, production preparation, and other work can be carried out in parallel.
Support technological innovation, improve product appearance design| it is conducive to optimize the product design, industrial design is especially important for that.
Reduce the costly design flaws|Prototyping allows product designers to identify potential product safety and/or compliance issues. From form to function, this stage is where you can get to the root of any risk factors involved in your design. Multiplied to reduce the cost of new product development .
Although many eyes can view the prototype design, quality control is still a significant downside for rapid prototyping. Whether the prototype is outsourced or made in-house, the prototype is always created based on the specifications. When you are producing something within a limited period, quality control is often neglected.Rapid prototyping technology can also limit options. While there is a wide array of manufacturing techniques that you can employ, there are also limitations. One of which is the inability to rapidly create a prototype with many moving parts that would interlock and function together. Because of these, complicated projects should not use rapid prototyping as their method. Prototyping will be additional development costs. Although rapid prototyping is now smaller, affordable, and more sustainable, it still presents an additional expense to the companies. Even if the companies outsource their rapid prototyping, it will still be an added cost.
Lack of accuracy – If the function of the product relies heavily on the accuracy of the parts, then rapid prototype parts and assembly might not be able to f the same accuracy.Reduced material properties like surface finish and strength.
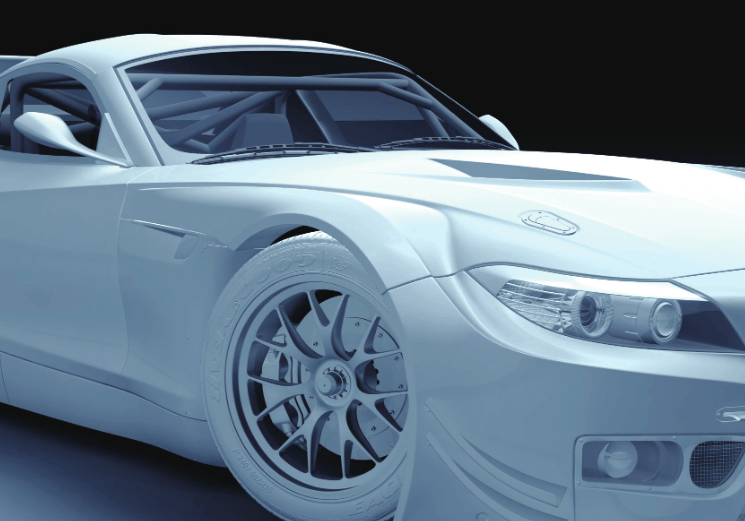

APPLICATION
The industries most likely to make use of rapid prototyping services include healthcare, transportation, consumer goods, and manufacturing.Rapid prototyping is also commonly applied in software engineering to try out new business models and application architectures such as Aerospace, Automotive, Financial Services, Product development.Aerospace design and industrial teams rely on prototyping in order to create new AM methodologies in the industry. Using SLA they can quickly make multiple versions of their projects in a few days and begin testing quicker.Rapid Prototyping allows designers to provide an accurate idea of how the finished product will turn out before putting too much time and money into the prototype. 3D printing being used for Rapid Prototyping allows for Industrial 3D printing to take place. With this, you could have large-scale moulds to spare parts being pumped out quickly within a short period of time.
HOW TO SELECT RAPID PROTOTYPING ?
The primary factors to consider are: Expected product quality|a rough design or functioning prototype Product fidelity |desired look and feel of the manufactured item Part complexity|for greater complexity, more precise rapid prototyping tools should be used
Purpose, Quality, Quantity, Complexity & Cost. The success or failure of a prototype depends on your selection of rapid prototyping processes for the new product development.
Purpose, Quality, Quantity, Complexity & Cost. The success or failure of a prototype depends on your selection of rapid prototyping processes for the new product development.
Technical feature for Rapid Prototyping
Fast manufacturing| RP technology is an effective means to carry out complex prototype or parts manufacturing in concurrent engineering, which can make product design and mold production synchronous, so as to improve the efficiency of enterprise research and development, shorten the product design cycle, greatly reduce the cost and risk of new product development, especially suitable for small size, special-shaped products.
Integration of CAD/CAM technology|Design and manufacturing integration has always been a difficulty, computer aided process (CAPP) at the present stage due to the complete seamless connection with CAD, CAM, this is also restricted manufacturing information has been one of the difficulties, and rapid prototyping technology integration CAD, CAM, laser technology, numerical control technology, chemical engineering, materials engineering and other technologies, Make the concept of integration of design and manufacturing perfect realization.
Complete reproduction of 3D data|The parts completed by rapid prototyping can completely reproduce the three-dimensional modeling. No matter the special-shaped surface on the outer surface or the special-shaped hole in the inner cavity, the modeling can be truly and accurately completed. Basically, it is no longer necessary to repair with the help of external equipment.
A wide variety of molding materialsThere are many kinds of materials used on all kinds of RP equipment, resin, nylon, plastic, paraffin, paper and metal or ceramic powder, basically meet the mechanical properties of the vast majority of products on the material needs.
Create significant economic benefits| Compared with the traditional machining method, the development cost is saved more than 10 times. Similarly, rapid prototyping technology shortens the product development cycle of the enterprise, so that the problem of repeatedly modifying the design scheme in the process of new product development is greatly reduced, and basically eliminates the problem of modifying the mold. The economic benefits created are obvious.
Wide range of application industries| RP technology after years of development, technology has basically formed a set of system, similarly, can be used in the industry is gradually expanded, from product design to mold design and manufacturing, materials engineering, medical research, culture and art, architectural engineering and so on are gradually using RP technology, so that RP technology has a broad prospect.
Integration of CAD/CAM technology|Design and manufacturing integration has always been a difficulty, computer aided process (CAPP) at the present stage due to the complete seamless connection with CAD, CAM, this is also restricted manufacturing information has been one of the difficulties, and rapid prototyping technology integration CAD, CAM, laser technology, numerical control technology, chemical engineering, materials engineering and other technologies, Make the concept of integration of design and manufacturing perfect realization.
Complete reproduction of 3D data|The parts completed by rapid prototyping can completely reproduce the three-dimensional modeling. No matter the special-shaped surface on the outer surface or the special-shaped hole in the inner cavity, the modeling can be truly and accurately completed. Basically, it is no longer necessary to repair with the help of external equipment.
A wide variety of molding materialsThere are many kinds of materials used on all kinds of RP equipment, resin, nylon, plastic, paraffin, paper and metal or ceramic powder, basically meet the mechanical properties of the vast majority of products on the material needs.
Create significant economic benefits| Compared with the traditional machining method, the development cost is saved more than 10 times. Similarly, rapid prototyping technology shortens the product development cycle of the enterprise, so that the problem of repeatedly modifying the design scheme in the process of new product development is greatly reduced, and basically eliminates the problem of modifying the mold. The economic benefits created are obvious.
Wide range of application industries| RP technology after years of development, technology has basically formed a set of system, similarly, can be used in the industry is gradually expanded, from product design to mold design and manufacturing, materials engineering, medical research, culture and art, architectural engineering and so on are gradually using RP technology, so that RP technology has a broad prospect.



